Accessing shared folders on Ubuntu often relies on the SMB (Server Message Block) protocol, also referred to as CIFS (Common Internet File System). It is broadly adopted for cross-platform file sharing across Windows, macOS, and Linux systems.
In Ubuntu, the SAMBA package seamlessly integrates SMB and CIFS functionality into the GNOME Files application, which simplifies the process of discovering and mounting network shares. This setup is particularly valuable for organizations with numerous systems requiring dependable access to shared resources.
Employing the built-in features of GNOME ensures a straightforward interface for identifying remote hosts and handling user credentials. The combination of stable protocols, up-to-date packages, and careful configuration offers secure connections and efficient file operations.
Steps to access SMB or CIFS shares from Ubuntu Desktop (GNOME):
- Open the Files application.
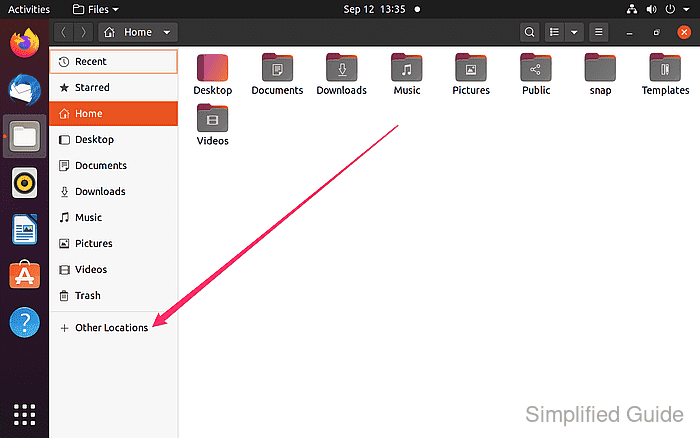
- Navigate to the “Other Locations” section from the sidebar menu.
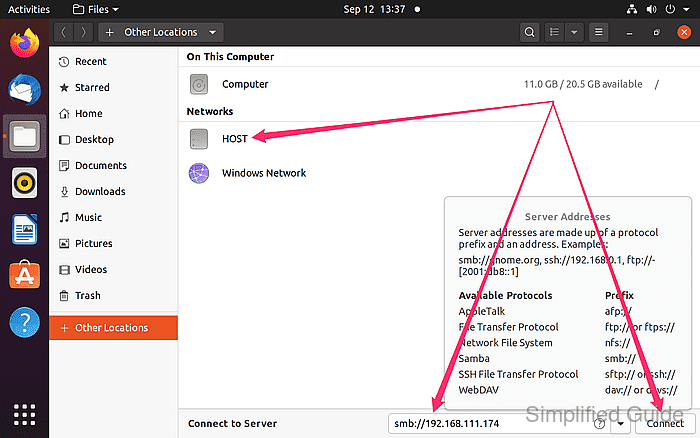
- Locate the network hosts under the “Networks” section or enter the host's IP address with the smb: prefix and click Connect.
 - Choose the shared folder you wish to access.
- Choose the shared folder you wish to access. 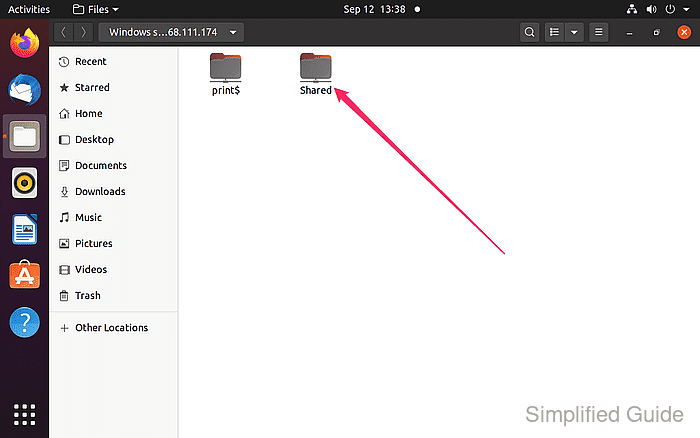 - Select “Connect” with Anonymous selected or enter login credentials if required.
- Select “Connect” with Anonymous selected or enter login credentials if required. 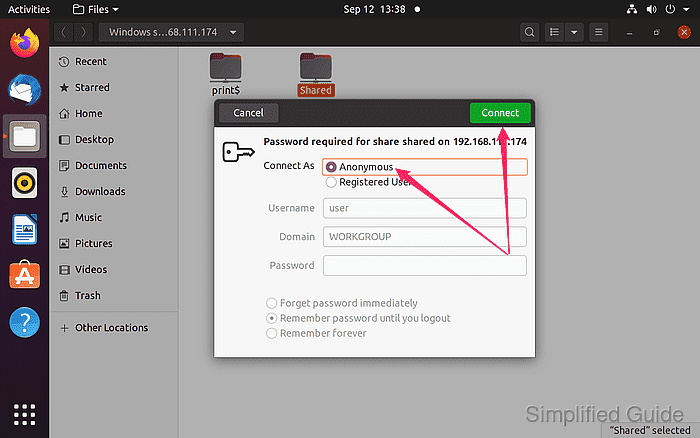
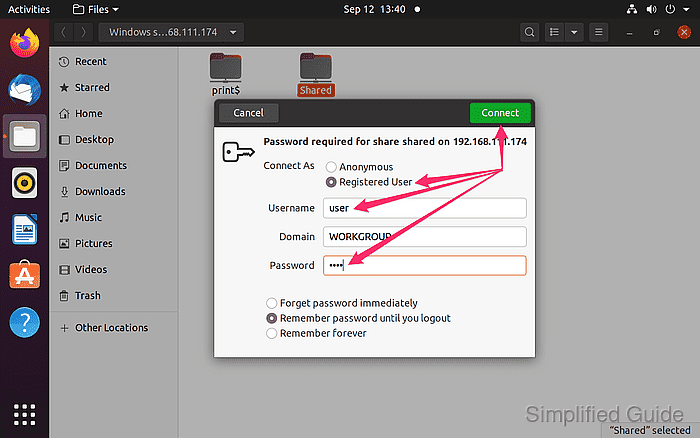 - Access the files and folders provided by the remote host.
- Access the files and folders provided by the remote host. 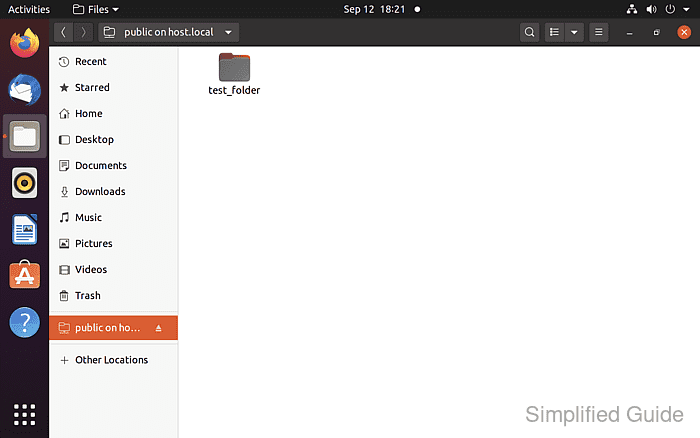 - Unmount the shared folder by clicking the eject icon when finished.
- Unmount the shared folder by clicking the eject icon when finished. 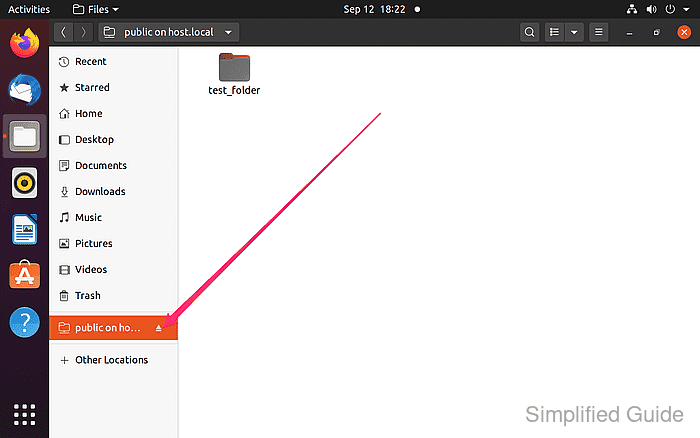
This guide is tested on Ubuntu:
Version Code Name 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish 23.10 Mantic Minotaur 24.04 LTS Noble Numbat

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
