Directory listing exposes file names and directory structure when a URL maps to a directory that lacks a default index page, turning a minor misconfiguration into an information leak for backups, source files, and internal assets.
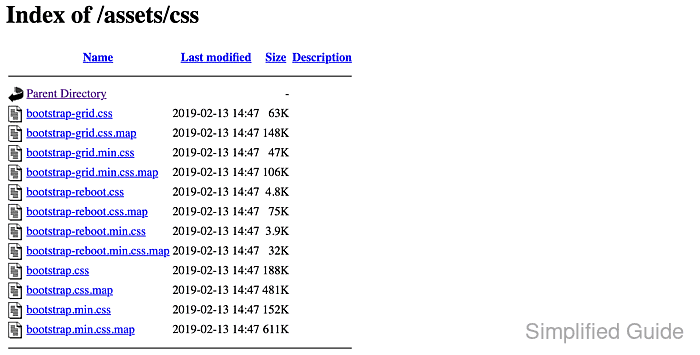
Apache selects a directory response using DirectoryIndex from mod_dir and generates a listing only when mod_autoindex is loaded and the directory permits Options Indexes with no matching index file present.
Commands and paths below assume Ubuntu or Debian with /etc/apache2/ layouts and the apache2 systemd unit, and the same controls apply elsewhere with different file locations and a httpd service name.
Related: How to restrict access to specific directories in Apache
Related: How to deny access to sensitive files in Apache
Related: How to disable Apache directory listing in cPanel
Adding more filenames to DirectoryIndex reduces accidental exposure, but a missing index file still triggers listing when Indexes is enabled.
Methods to disable directory listing in Apache:
Prefer Options -Indexes in a VirtualHost or <Directory> block for production, and reserve disabling mod_autoindex for servers where listings should never work anywhere.
For those using platforms like cPanel, there are platform-specific methods to disable Apache's directory listing.
Steps to disable directory listing in Apache:
Disable Apache directory listing by disabling autoindex module
Disabling mod_autoindex blocks auto-generated directory listings across all hosted sites, regardless of per-directory settings.
- Open a terminal with sudo privileges.
- Disable mod_autoindex with a2dismod.
$ sudo a2dismod --force autoindex Module autoindex disabled. To activate the new configuration, you need to run: systemctl restart apache2
Any URL that previously relied on an auto-generated listing will return an error after mod_autoindex is disabled.
On platforms without a2dismod, comment out the LoadModule autoindex_module line in the main Apache configuration and restart the service.
- Validate the Apache configuration syntax.
$ sudo apache2ctl configtest Syntax OK
- Restart the Apache service to unload the module.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
- Request a directory URL without a default index file to confirm listing is blocked.
$ curl -i -H 'Host: host.example.net' http://127.0.0.1/downloads/ HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found Date: Sat, 10 Jan 2026 05:43:36 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.58 (Ubuntu) Content-Length: 278 Content-Type: text/html; charset=iso-8859-1 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN"> <html><head> <title>404 Not Found</title> </head><body> <h1>Not Found</h1> <p>The requested URL was not found on this server.</p> <hr> <address>Apache/2.4.58 (Ubuntu) Server at host.example.net Port 80</address> </body></html>
Replace host.example.net and the path with a directory that has no DirectoryIndex file present. A 403 or 404 response confirms listing is blocked when no index file exists.
Disable Apache directory listing via Directory's Options directive
Setting Options -Indexes is the most common hardening approach because it disables browsing for a specific directory while keeping mod_autoindex available for other sites.
- Open the relevant VirtualHost or global configuration file in a text editor.
$ sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
The change can be placed inside a VirtualHost file or in /etc/apache2/apache2.conf/ for a global default.
- Locate the <Directory> block that matches the web root path.
<Directory /var/www/html/mysite> Options Indexes FollowSymLinks </Directory>
- Disable directory indexing by setting -Indexes in the Options line.
<Directory /var/www/html/mysite> Options -Indexes +FollowSymLinks </Directory>
Use relative + and - prefixes consistently when modifying Options values.
- Validate the Apache configuration syntax.
$ sudo apache2ctl configtest Syntax OK
- Reload the Apache service to apply the configuration change.
$ sudo systemctl reload apache2
- Request a directory URL without a default index file to confirm listing is blocked.
$ curl -i -H 'Host: host.example.net' http://127.0.0.1/mysite/ HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden Date: Sat, 10 Jan 2026 05:43:31 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.58 (Ubuntu) Content-Length: 281 Content-Type: text/html; charset=iso-8859-1 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN"> <html><head> <title>403 Forbidden</title> </head><body> <h1>Forbidden</h1> <p>You don't have permission to access this resource.</p> <hr> <address>Apache/2.4.58 (Ubuntu) Server at host.example.net Port 80</address> </body></html>
A 403 Forbidden response is typical when directory listing is disabled and no index file exists.
Disable Apache directory listing using .htaccess
A .htaccess file can disable listings in a specific directory when server-wide configuration access is unavailable, but it only works when AllowOverride permits Options directives.
- Confirm the directory allows .htaccess overrides for Options.
<Directory /var/www/html/mysite> AllowOverride Options </Directory>
Enabling AllowOverride All increases per-request filesystem checks and can permit unsafe directives if the directory is writable by untrusted users.
- Create or edit the .htaccess file in the target directory.
$ sudo vi /var/www/html/mysite/.htaccess
- Disable directory indexing inside .htaccess.
Options -Indexes
Changes to .htaccess apply on the next request when AllowOverride permits the directive.
The .htaccess directive is ignored when AllowOverride does not permit Options.
- Request a directory URL without a default index file to confirm listing is blocked.
$ curl -i -H 'Host: host.example.net' http://127.0.0.1/mysite/ HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden Date: Sat, 10 Jan 2026 05:43:56 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.58 (Ubuntu) Content-Length: 281 Content-Type: text/html; charset=iso-8859-1 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN"> <html><head> <title>403 Forbidden</title> </head><body> <h1>Forbidden</h1> <p>You don't have permission to access this resource.</p> <hr> <address>Apache/2.4.58 (Ubuntu) Server at host.example.net Port 80</address> </body></html>
- Reload the Apache service after editing AllowOverride in server configuration.
$ sudo systemctl reload apache2

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
