The gpart utility recovers lost or deleted partitions by scanning for existing filesystems and identifying partition boundaries. It is essential for data recovery on Ubuntu when the partition table is corrupted or missing. Its design allows you to restore critical partition structures on various types of storage devices.
In many Ubuntu installations, gpart is not included by default. It can be acquired through the apt package manager, which provides a reliable method for downloading and installing the latest version. This ensures compatibility with both legacy MBR and modern GPT partitioning schemes.
Once installed, gpart operates through the command line. It accepts different scan parameters to fine-tune recovery, providing flexibility for complex disk configurations. With its ability to detect and rebuild partitions, gpart remains a trusted solution in data recovery scenarios.
Steps to install gpart on Ubuntu:
- Launch terminal.
- Update apt's package list.
$ sudo apt update Hit:1 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security InRelease Hit:2 http://jp.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal InRelease Get:3 http://jp.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates InRelease [111 kB] Get:4 http://jp.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-backports InRelease [98.3 kB] Fetched 210 kB in 1s (193 kB/s) Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done All packages are up to date.
- Install the gpart package using apt.
$ sudo apt install --assume-yes gpart Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following NEW packages will be installed: gpart 0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Need to get 35.2 kB of archives. After this operation, 82.9 kB of additional disk space will be used.
- Start using gpart to recover lost or deleted partition tables.
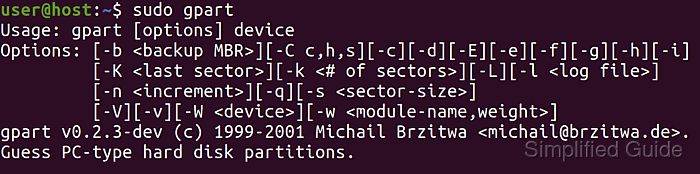
$ sudo gpart Usage: gpart [options] device Options: [-b <backup MBR>][-C c,h,s][-c][-d][-E][-e][-f][-g][-h][-i] [-K <last sector>][-k <# of sectors>][-L][-l <log file>] [-n <increment>][-q][-s <sector-size>] [-V][-v][-W <device>][-w <module-name,weight>] gpart v0.2.3-dev (c) 1999-2001 Michail Brzitwa <michail@brzitwa.de>. Guess PC-type hard disk partitions.More options for gpart.
Options: -b Save a backup of the original MBR to specified file. -C Set c/h/s to be used in the scan. -c Check/compare mode. -d Do not start the guessing loop. -E Do not try to identify extended partition tables. -e Do not skip disk read errors. -f Full scan. -g Do not try to get the disk geometry. -h Show this help. -i Run interactively (ask for confirmation). -K Scan only up to given sector. -k Skip sectors before scan. -L List available modules and their weights, then exit. -l Logfile name. -n Scan increment: number or 's' sector, 'h' head, 'c' cylinder. -q Run quiet (however log file is written if specified). -s Sector size to use (disable sector size probing). -V Show version. -v Verbose mode. Can be given more than once. -W Write guessed primary partition table to given device or file. -w Weight factor of module.
This guide is tested on Ubuntu:
| Version | Code Name |
|---|---|
| 22.04 LTS | Jammy Jellyfish |
| 23.10 | Mantic Minotaur |
| 24.04 LTS | Noble Numbat |

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
