Managing the passphrase of an SSH private key determines how much damage an exposed key file can cause if it is copied from disk or backups. A strong passphrase ensures that access to the private key file alone is not enough to establish SSH sessions using that identity.
In OpenSSH, public and private keys form a pair used with the publickey authentication method. The public key is placed on servers, while the private key remains on the client and can be encrypted at rest with a passphrase using ssh-keygen. Changing or removing the passphrase re-encrypts the same underlying key material, so authorized keys on servers do not need to be updated.
Because ssh-keygen -p rewrites the private key file in place, keeping a backup copy of the original key reduces the risk of accidental data loss. Removing a passphrase eliminates an important protection boundary, especially on shared or mobile systems, and any running ssh-agent should be reloaded so that cached keys match the new passphrase state.
Related: How to generate SSH key pairs
Related: How to set up passwordless SSH authentication
Methods to manage passphrase of an SSH key.
Steps to add a passphrase to an SSH key:
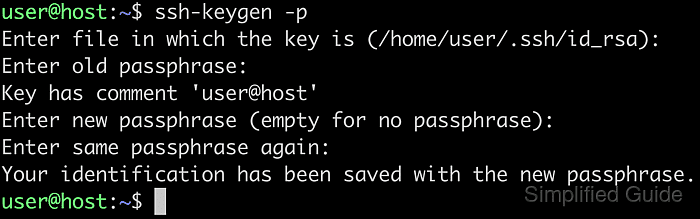
- Run ssh-keygen with -p option to start editing an existing private key.
$ ssh-keygen -p
The -p option changes the passphrase on an existing private key without generating a new key pair.
- Specify the location of the SSH private key when prompted, or press [ENTER] to accept the default path.
Enter file in which the key is (/home/user/.ssh/id_ed25519):
Typical user keys reside under /home/user/.ssh with names such as id_rsa or id_ed25519.
- Enter the existing passphrase if the key is already protected, or press [ENTER] when the key is unencrypted.
Enter old passphrase:
- Review the key comment shown to confirm that the intended key is being edited.
Key has comment 'user@host'
- Enter a new passphrase for the key twice at the prompts.
Enter new passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again:
- Observe the confirmation message indicating that the private key has been re-encrypted with the new passphrase.
Your identification has been saved with the new passphrase.
- Verify that the key now requires the new passphrase by printing its public form.
$ ssh-keygen -y -f /home/user/.ssh/id_ed25519 Enter passphrase: ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIHbe3AdFxFsytQyYz0EVjNSpwEoiW1h3UyXj9PybQFLM user@host
A prompt for the new passphrase followed by an SSH public key line confirms that the private key passphrase was applied successfully.
Steps to change an SSH key passphrase:
- Run ssh-keygen with -p option to update the passphrase of an existing private key.
$ ssh-keygen -p
The same command is used for adding, changing, or removing a passphrase; the interaction at the prompts determines the outcome.
- Specify the location of the SSH private key when prompted, or accept the default if the key uses the standard name and directory.
Enter file in which the key is (/home/user/.ssh/id_ed25519):
The default path typically points to the primary key for the current account under /home/user/.ssh.
- Enter the current passphrase for the private key.
Enter old passphrase:
An incorrect passphrase prevents ssh-keygen from decrypting and rewriting the key, and repeated failures can suggest that the wrong file is being modified.
- Confirm the key comment displayed for the selected key.
Key has comment 'user@host'
- Enter the new passphrase for the key twice at the prompts.
Enter new passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again:
Updating the passphrase does not change the public key, so servers using the existing authorized_keys entries continue to accept this key.
- Check the confirmation message indicating that the private key has been saved with the updated passphrase.
Your identification has been saved with the new passphrase.
- Confirm that the new passphrase works by printing the public key from the private key file.
$ ssh-keygen -y -f /home/user/.ssh/id_ed25519 Enter passphrase: ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIHbe3AdFxFsytQyYz0EVjNSpwEoiW1h3UyXj9PybQFLM user@host
Successful decryption with the new passphrase followed by valid public key output shows that the change took effect.
Steps to remove a passphrase from an SSH key:
- Run ssh-keygen with -p option to modify the passphrase protection of the private key.
$ ssh-keygen -p
- Specify the location of the SSH private key when prompted, or accept the default path.
Enter file in which the key is (/home/user/.ssh/id_ed25519):
- Enter the existing passphrase for the private key.
Enter old passphrase:
- Confirm the key comment displayed for the selected key.
Key has comment 'user@host'
- Press [ENTER] twice at the new passphrase prompts without typing any passphrase so that the key is saved unprotected.
Enter new passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again:
Removing the passphrase allows anyone with read access to the private key file to authenticate as that key, which significantly reduces security on multi-user or unsecured systems.
- Check the confirmation message indicating that the private key has been written without a passphrase.
Your identification has been saved with the new passphrase.
- Verify that the key no longer prompts for a passphrase when deriving the public key.
$ ssh-keygen -y -f /home/user/.ssh/id_ed25519 ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIHbe3AdFxFsytQyYz0EVjNSpwEoiW1h3UyXj9PybQFLM user@host
Absence of a passphrase prompt before the public key output indicates that the private key is no longer encrypted.

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
