SSH (Secure Shell) provides encrypted access to remote systems and is widely used for administration, backups, and file exchange across networks. Secure file copying avoids exposing data or credentials in transit, which is critical when moving configuration files, application builds, or database exports between environments.
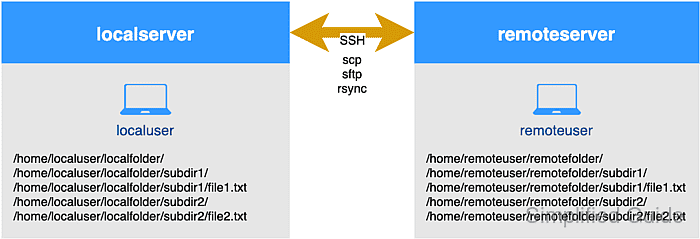
SSH supports several file transfer mechanisms over the same secure transport, including scp for one-shot copies, sftp for interactive transfers, rsync for efficient synchronization, and sshfs for mounting remote filesystems. Each approach uses the same underlying authentication and encryption but offers different workflows for moving data.
Reliable transfers depend on working SSH connectivity, correct permissions on both ends, and sufficient bandwidth for the data volume being moved. The examples use typical /home-based paths, a local account and a remote account as shown in the diagram, and a remote host reachable over standard SSH, with all commands run from a terminal on the local system; the same patterns apply to other directories and hosts with adjusted paths and usernames.
Steps to copy files remotely using SSH:
Ensure working SSH access to the remote server and sufficient permissions on the involved files and directories to avoid failed transfers or partial copies.
Methods for remote file transfer using SSH:
Transfer file using scp
scp (Secure Copy) is a straightforward command-line tool for copying files between local and remote systems over SSH. The syntax resembles the cp command but accepts a user and host prefix, which makes it well-suited to quick, non-interactive transfers.
Because scp does not track which files already exist or are up to date on the destination, it is better suited to occasional copies than to large, repetitive synchronizations. For small numbers of files, configuration pushes, or ad‑hoc downloads, it provides a simple and dependable option.
- Confirm SSH access to the remote server using the account intended for file transfers.
$ ssh user@host.example.net "echo OK" OK
- Copy a single file from the local system to the remote host using scp.
$ scp /home/user/localfolder/subdir1/file1.txt user@host.example.net:/home/user/remotefolder/subdir1/ file1.txt 100% 17 135.0KB/s 00:00
- Copy a single file from the remote host to the local system using scp.
$ scp user@host.example.net:/home/user/remotefolder/subdir1/file1.txt /home/user/localfolder/subdir1/ file1.txt 100% 17 103.1KB/s 00:00
- Copy multiple files from the local system into the same remote directory with one scp command.
$ scp /home/user/localfolder/subdir1/file1.txt /home/user/localfolder/subdir2/file2.txt user@host.example.net:/home/user/remotefolder/ file1.txt 100% 17 144.8KB/s 00:00 file2.txt 100% 12KB 43.8MB/s 00:00
- Recursively transfer an entire local directory tree to the remote host using the -r option in scp.
$ scp -r /home/user/localfolder/ user@host.example.net:/home/user/remotefolder/ file2.txt 100% 12KB 43.9MB/s 00:00 file1.txt 100% 17 214.6KB/s 00:00
- Verify that the expected files exist on the remote side after the transfer.
$ ssh user@host.example.net "ls -R /home/user/remotefolder" /home/user/remotefolder: file1.txt file2.txt localfolder subdir1 subdir2 /home/user/remotefolder/localfolder: subdir1 subdir2 /home/user/remotefolder/localfolder/subdir1: file1.txt /home/user/remotefolder/localfolder/subdir2: file2.txt /home/user/remotefolder/subdir1: file1.txt /home/user/remotefolder/subdir2:
GUI programs such as WinSCP can transfer files between local and remote hosts using scp or sftp while providing drag‑and‑drop file management.
Transfer file using sftp
sftp (SSH File Transfer Protocol) provides an interactive shell over SSH for navigating directories and transferring files. The prompt accepts commands similar to traditional file managers, which makes it convenient for exploring remote paths and moving several files in a single session.
The interactive nature of sftp also supports batch uploads or downloads and can resume interrupted transfers in many cases, making it practical when the exact filenames or locations are not fully known in advance.
- Start an sftp session by connecting to the remote server.
$ sftp user@host.example.net sftp>
- List and navigate directories on the remote server using commands such as ls and cd at the sftp prompt.
Connected to host.example.net. sftp> ls /home/user/remotefolder/ /home/user/remotefolder/subdir1 /home/user/remotefolder/subdir2 sftp> cd /home/user/remotefolder/subdir1 sftp> pwd Remote working directory: /home/user/remotefolder/subdir1
- Download a file from the remote server to a local directory with the get command.
sftp> get /home/user/remotefolder/subdir1/file1.txt /home/user/localfolder/subdir1/ Fetching /home/user/remotefolder/subdir1/file1.txt to /home/user/localfolder/subdir1/file1.txt
- Upload a local file to the remote server with the put command.
sftp> put /home/user/localfolder/subdir1/file1.txt /home/user/remotefolder/subdir1/ Uploading /home/user/localfolder/subdir1/file1.txt to /home/user/remotefolder/subdir1/file1.txt
- End the sftp session when transfers are complete.
sftp> bye
- Confirm that the transferred file exists on the local system after a download or on the remote system after an upload.
$ ls /home/user/localfolder/subdir1/ file1.txt
Transfer file using rsync
rsync synchronizes files and directories between local and remote systems while sending only the differences between source and destination. This behavior greatly reduces traffic for repeated transfers, which is useful for backups, mirrors, and deployment trees.
When used with a destination in the form user@host.example.net:/path, rsync runs over SSH and preserves permissions, ownership, timestamps, and symbolic links when requested. Using the -e option explicitly selects ssh as the remote shell, while double‑colon syntax (for example, host.example.net::module/path) targets an rsyncd daemon instead.
- Verify that network access and SSH authentication work between the local host and the remote server.
$ ssh user@host.example.net "hostname" host
- Synchronize a local directory to a remote directory over SSH, deleting files on the destination that no longer exist at the source.
$ rsync -av --delete -e ssh /home/user/localfolder/ user@host.example.net:/home/user/remotefolder/ sending incremental file list deleting localfolder/subdir2/file2.txt deleting localfolder/subdir2/ deleting localfolder/subdir1/file1.txt deleting localfolder/subdir1/ deleting localfolder/ deleting file2.txt deleting file1.txt ./ subdir1/ subdir2/file2.txt sent 12,504 bytes received 199 bytes 25,406.00 bytes/sec total size is 12,305 speedup is 0.97
- Mirror a remote directory to a local directory using the same flags in reverse.
$ rsync -av --delete -e ssh user@host.example.net:/home/user/remotefolder/ /home/user/localfolder/ receiving incremental file list sent 22 bytes received 155 bytes 118.00 bytes/sec total size is 12,305 speedup is 69.52
- Transfer only files that are new or modified on the source by using the --update option so existing newer files on the destination remain unchanged.
$ rsync -av --update -e ssh /home/user/localfolder/ user@host.example.net:/home/user/remotefolder/ sending incremental file list sent 159 bytes received 14 bytes 346.00 bytes/sec total size is 12,305 speedup is 71.13
- Exclude specific patterns such as log files from synchronization with the --exclude option.
$ rsync -av --exclude '*.log' -e ssh /home/user/localfolder/ user@host.example.net:/home/user/remotefolder/ sending incremental file list sent 159 bytes received 14 bytes 346.00 bytes/sec total size is 12,305 speedup is 71.13
- Verify the result by listing key paths on the destination and checking that only the expected files are present.
$ ssh user@host.example.net "ls -R /home/user/remotefolder" /home/user/remotefolder: subdir1 subdir2 /home/user/remotefolder/subdir1: file1.txt /home/user/remotefolder/subdir2: file2.txt
Mount remote filesystem locally
sshfs mounts a remote directory over SSH so that remote files appear as part of the local filesystem. This approach allows normal tools such as cp, text editors, or backup programs to operate on remote data without special transfer commands.
Mounting a remote filesystem is particularly useful for working on many small files or for tools that are not SSH‑aware but can operate on local paths.

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
