Exposing an SSH server to the internet attracts automated bots that constantly attempt password guesses and key-based logins. Persistent brute force activity wastes resources, floods logs, and increases the chance of a compromised account if credentials are weak. Automatically detecting and blocking abusive sources keeps remote administration available while reducing noise.
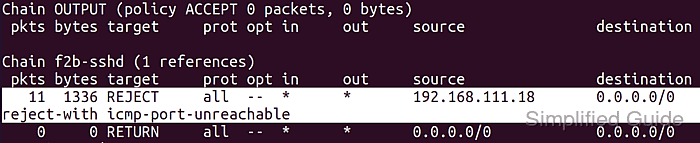
On Linux, tools like fail2ban monitor authentication logs from sshd and translate suspicious patterns into firewall rules. When a source exceeds a defined number of failures within a time window, its IP address is added to a temporary ban list via iptables, nftables, or the distribution firewall backend. Thresholds for retries, ban duration, and matching patterns are controlled per jail section such as the built-in sshd jail.
Deploying automatic bans demands careful tuning to avoid blocking valid administrators, especially when working behind NAT gateways, load balancers, or jump hosts that share a single public address. Configuration should live in /etc/fail2ban/jail.local to survive package upgrades, and changes must be validated before relying on them in production. Testing from a secondary session prevents accidental lockouts while new rules are being applied.
Steps to protect against SSH brute force attacks:
- Open a terminal on the Linux server with access to sudo privileges.
$ whoami user $ sudo -n -l sudo: a password is required
- Install fail2ban from the distribution package repository so that SSH login attempts can be monitored and banned.
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt install --assume-yes fail2ban Hit:1 http://ports.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-ports noble InRelease Hit:2 http://ports.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-ports noble-updates InRelease Hit:3 http://ports.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-ports noble-backports InRelease Hit:4 http://ports.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-ports noble-security InRelease Reading package lists... Building dependency tree... Reading state information... fail2ban is already the newest version (1.0.2-3ubuntu0.1). 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 10 not upgraded.
On RHEL and CentOS use sudo dnf install --assume-yes fail2ban, and on openSUSE use sudo zypper install --no-confirm fail2ban.
- Enable the fail2ban service so bans persist across reboots and take effect immediately.
$ sudo systemctl enable --now fail2ban $ sudo systemctl status fail2ban ● fail2ban.service - Fail2Ban Service Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/fail2ban.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Sun 2026-01-11 05:47:00 +08; 35s ago Docs: man:fail2ban(1) Main PID: 16648 (fail2ban-server) Tasks: 5 (limit: 4546) Memory: 19.8M (peak: 20.3M) CPU: 184ms CGroup: /system.slice/fail2ban.service └─16648 /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/fail2ban-server -xf start ##### snipped ##### - Copy the default /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf configuration to /etc/fail2ban/jail.local so custom settings survive package upgrades.
$ sudo cp /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
The .local file overrides matching sections from the default configuration while remaining untouched by package updates.
- Edit the /etc/fail2ban/jail.local file to enable and tune the sshd jail for blocking repeated authentication failures.
/etc/fail2ban/jail.local [sshd] enabled = true port = ssh filter = sshd logpath = /var/log/auth.log maxretry = 5 findtime = 600 bantime = 3600
Setting maxretry too low or bantime excessively high can block legitimate administrators, especially when many logins pass through a shared NAT address.
- Restart the fail2ban service to load the new configuration and activate the updated sshd jail.
$ sudo systemctl restart fail2ban
Restarting fail2ban while relying solely on remote SSH access can briefly remove existing bans and apply new ones, so maintain an alternative access path when changing production settings.
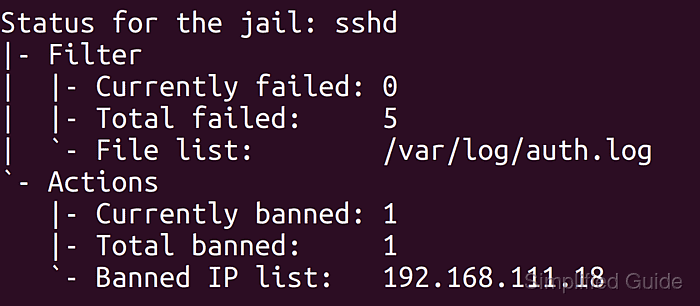
- Check the status of the sshd jail to confirm that log files are being read and that ban counters are tracked.
$ sudo fail2ban-client status sshd Status for the jail: sshd |- Filter | |- Currently failed: 0 | |- Total failed: 0 | `- Journal matches: _SYSTEMD_UNIT=sshd.service + _COMM=sshd `- Actions |- Currently banned: 0 |- Total banned: 0 `- Banned IP list:
A non-zero value for Currently failed or Total banned indicates that fail2ban is actively monitoring and acting on failed logins.
- Display the fail2ban-client built-in help for an overview of available management commands.
$ sudo fail2ban-client --help Usage: fail2ban-client [OPTIONS] <COMMAND> Fail2Ban v1.0.2 reads log file that contains password failure report and bans the corresponding IP addresses using firewall rules. Options: -c, --conf <DIR> configuration directory -s, --socket <FILE> socket path -p, --pidfile <FILE> pidfile path --pname <NAME> name of the process (main thread) to identify instance (default fail2ban-server) --loglevel <LEVEL> logging level --logtarget <TARGET> logging target, use file-name or stdout, stderr, syslog or sysout. --syslogsocket auto|<FILE> -d dump configuration. For debugging --dp, --dump-pretty dump the configuration using more human readable representation -t, --test test configuration (can be also specified with start parameters) -i interactive mode -v increase verbosity -q decrease verbosity -x force execution of the server (remove socket file) -b start server in background (default) -f start server in foreground --async start server in async mode (for internal usage only, don't read configuration) --timeout timeout to wait for the server (for internal usage only, don't read configuration) ##### snipped ##### - Confirm that offending hosts are banned after repeated failed logins by rechecking the sshd jail status from another session.
$ sudo fail2ban-client status sshd Status for the jail: sshd ##### snipped ##### |- Currently banned: 1 |- Total banned: 1 `- Banned IP list: 203.0.113.10

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
