Backing up an optical disk on a Linux system preserves installers, media, and archived data in a single ISO file that is easy to store and reuse. An ISO image duplicates the layout and content of a CD, DVD, or Blu-ray so the data stays available even when the original media becomes scratched or the drive is removed. Creating a local copy also simplifies virtual machine usage and network-based installations.
Under Linux, an optical drive usually appears as a block device such as /dev/sr0 that exposes fixed-size sectors from the disk. Reading this device from start to end produces the same byte-for-byte stream the drive would present to the operating system while the disk is inserted. Using a low-level copy tool against the raw device makes it possible to capture the entire filesystem and boot structures into a single image file.
Creating an ISO image of a disk requires sufficient free storage for the full size of the medium and access to sudo for reading the raw device. Incorrect parameters in copy commands can overwrite data or produce incomplete backups if the target path is wrong or the disk contains unreadable sectors. Verifying disk size beforehand and comparing checksums after the copy helps avoid silent corruption and confirms the backup is reliable.
Steps to create image from optical media in Linux:
- Open a terminal on the Linux system with an account that can use sudo.
$ whoami root
- Identify the device name of the optical drive.
$ sudo losetup --find --show --read-only /root/sg-work/iso-demo/demo.iso /dev/loop1
On physical systems, the optical drive typically appears as sr0 with type rom; in virtual or lab environments, a loop device like loop1 can be used to simulate the raw disk.
- Check the raw size of the disk through its block device.
$ sudo blockdev --getsize64 /dev/loop1 360448
The reported size (bytes) indicates the minimum free space required for the resulting ISO image.
- Verify that the target filesystem has enough free space for the ISO image.
$ df -h /root Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on overlay 1.8T 17G 1.7T 1% /
Choose a directory with available space greater than or equal to the size reported for the source device.
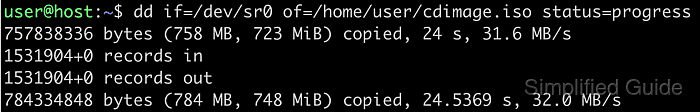
- Create a sector-by-sector ISO image from the optical disk using dd.
$ sudo dd if=/dev/loop1 of=/root/sg-work/iso-demo/demo-copy.iso status=progress 704+0 records in 704+0 records out 360448 bytes (360 kB, 352 KiB) copied, 0.000815497 s, 442 MB/s
An incorrect of= target in the dd command can overwrite existing data and cause irreversible file loss.
- Compare checksums of the raw device and the ISO image to confirm a bit-identical copy.
$ sudo md5sum /dev/loop1 /root/sg-work/iso-demo/demo-copy.iso 1957a123cc4fed0ff92a84cb9738a0bc /dev/loop1 1957a123cc4fed0ff92a84cb9738a0bc /root/sg-work/iso-demo/demo-copy.iso
Matching checksums confirm that the backup ISO image is an exact copy of the optical disk.
- Optionally mount the ISO image read-only to inspect its contents after creation.
$ sudo mkdir -p /mnt/iso $ sudo mount -o loop,ro /root/sg-work/iso-demo/demo-copy.iso /mnt/iso
Mounting the ISO image provides a quick visual confirmation that files and directory structure are present and readable.
- Unmount the ISO image from the temporary mount point when inspection is complete.
$ sudo umount /mnt/iso

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
