When troubleshooting web forms, API endpoints, or webhook callbacks, the difference between a working request and a failing one is often hidden in the POST body. Standard Apache access logs record the request line, status code, and timing, but omit payloads, leaving body-dependent bugs difficult to reproduce.
Logging request bodies in Apache is typically done with mod_dumpio, which dumps raw bytes from the request input and response output filter chains into the error log. With DumpIOInput enabled and the LogLevel for the dumpio module raised (commonly to trace7), each request that carries a body produces dumpio_in entries containing the received data.
Request bodies commonly include passwords, tokens, session identifiers, and personal data, so dumping them to logs is a high-risk debugging change that should be short-lived and tightly access-controlled. Because trace7 output can generate many log lines per request and fill disks quickly, revert the directives immediately after capturing the needed sample and confirm log rotation is functioning.
Steps to log POST request data in Apache:
- Enable the mod_dumpio module.
$ sudo a2enmod dump_io Enabling module dump_io. To activate the new configuration, you need to run: systemctl restart apache2
mod_dumpio writes to the error log, not the access log; the target file can be set per VirtualHost with the ErrorLog directive.
Platform Typical enablement Debian/Ubuntu layouts Enable with a2enmod dump_io. Platforms without a2enmod Load the module with LoadModule dumpio_module .../mod_dumpio.so (exact path varies by packaging). - Open the site's VirtualHost configuration file.
$ sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
On Debian-style layouts, /etc/apache2/sites-enabled usually contains symlinks pointing at /etc/apache2/sites-available.
- Add DumpIOInput plus a module-specific LogLevel inside the matching VirtualHost block.
<VirtualHost *:80> ##### snipped ##### DumpIOInput On DumpIOOutput Off LogLevel warn dumpio:trace7 </VirtualHost>
Directive Description DumpIOInput Enables input logging so request bodies (such as POST data) are written to the error log. DumpIOOutput Logs response output bytes when enabled; leaving it Off reduces noise and limits accidental data exposure. LogLevel Raises verbosity for dumpio without forcing a global log level increase; trace7 is extremely verbose. - Save the configuration file and exit the editor.
- Validate the Apache configuration syntax.
$ sudo apache2ctl -t Syntax OK
- Restart Apache to apply the changes.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
On Fedora, CentOS, and RHEL the service name is typically httpd (sudo systemctl restart httpd).
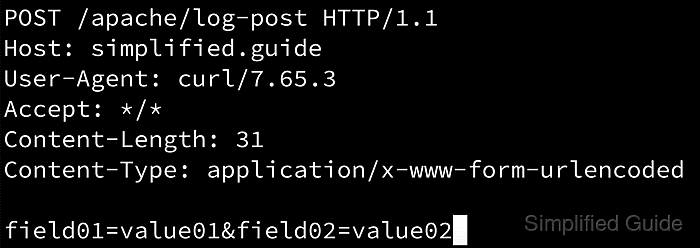
- Send a test POST request with a small body to the affected vhost.
$ curl --request POST --data "field01=value01&field02=value02" --silent --output /dev/null --write-out "%{http_code}\n" http://127.0.0.1/ 200 - Confirm the request body appears in the error log as a dumpio_in entry.
$ sudo grep -F "field01=value01" /var/log/apache2/error.log [Sat Jan 10 13:43:40.289489 2026] [dumpio:trace7] [pid 8262:tid 257537165750560] mod_dumpio.c(100): [client 127.0.0.1:47086] mod_dumpio: dumpio_in (data-HEAP): field01=value01&field02=value02
If the file path differs, check the ErrorLog directive in the active VirtualHost and read that log instead of /var/log/apache2/error.log.
- Revert the debug directives in the VirtualHost after capturing the needed sample.
<VirtualHost *:80> ##### snipped ##### LogLevel warn </VirtualHost>
Leaving DumpIOInput enabled risks logging credentials and personal data, and trace7 output can fill disks quickly on busy sites.
- Disable mod_dumpio after the debug session is complete.
$ sudo a2dismod dump_io Module dump_io disabled. To activate the new configuration, you need to run: systemctl restart apache2
Disabling the module while DumpIOInput directives remain in the config prevents Apache from starting with an “Invalid command” error.
- Restart Apache to apply the cleanup.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
