Installing Apache on Ubuntu or Debian provides a fast, standard way to host websites, reverse-proxy applications, or publish internal documentation from a well-supported web server.
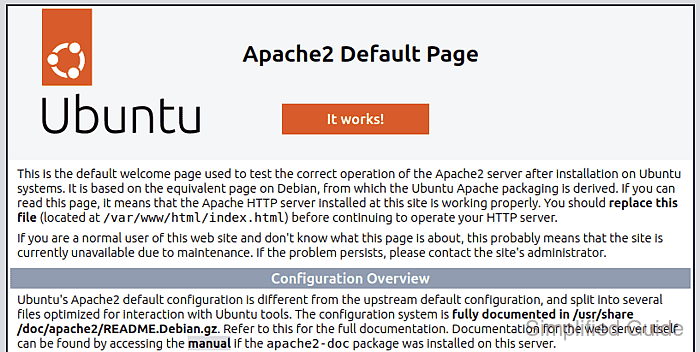
On these distributions, the Apache2 package ships a systemd service named apache2 plus a configuration layout under /etc/apache2 that separates global settings, enabled modules, and enabled virtual hosts. Helper commands such as a2enmod, a2dismod, a2ensite, and a2enconf manage symlinks between /etc/apache2/*-available and /etc/apache2/*-enabled, while apache2ctl validates configuration and performs graceful restarts.
Configuration mistakes can prevent apache2 from starting, so syntax checks should run before any reload or restart. Exposing ports 80 and 443 may require firewall changes, and a default install is reachable locally before DNS and TLS are configured.
Steps to install and customize Apache on Ubuntu and Debian:
- Open a terminal with sudo privileges.
- Update the apt package index.
$ sudo apt update WARNING: apt does not have a stable CLI interface. Use with caution in scripts. Get:1 http://ports.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-ports noble InRelease [256 kB] Get:2 http://ports.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-ports noble-updates InRelease [126 kB] Get:3 http://ports.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-ports noble-backports InRelease [126 kB] Get:4 http://ports.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-ports noble-security InRelease [126 kB] ##### snipped ##### Reading package lists... Building dependency tree... Reading state information... 9 packages can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see them.
- Install the Apache2 package and its dependencies.
$ sudo apt install --assume-yes apache2 WARNING: apt does not have a stable CLI interface. Use with caution in scripts. Reading package lists... Building dependency tree... Reading state information... apache2 is already the newest version (2.4.58-1ubuntu8.8). 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 9 not upgraded.
- Confirm the apache2 service is running.
$ sudo systemctl status apache2 ● apache2.service - The Apache HTTP Server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/apache2.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2025-12-29 03:05:47 UTC; 14s ago Docs: https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/ Process: 2204 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/apachectl start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 2207 (apache2) Tasks: 6 (limit: 9396) Memory: 14.8M (peak: 15.7M) CPU: 28ms CGroup: /system.slice/apache2.service ├─2207 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start ├─2211 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start ##### snipped #####Use journalctl -u apache2 and /var/log/apache2/error.log for recent startup errors.
- Enable the Apache2 service to start automatically on boot.
$ sudo systemctl enable apache2 Synchronizing state of apache2.service with SysV service script with /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install. Executing: /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable apache2
- Enable the rewrite module when URL rewriting is required.
$ sudo a2enmod rewrite Enabling module rewrite. To activate the new configuration, you need to run: systemctl restart apache2
Common add-ons include headers, ssl, proxy, and http2.
- Verify that the rewrite module is loaded.
$ sudo apache2ctl -M | grep rewrite rewrite_module (shared)
- Display the default virtual host configuration to find DocumentRoot and logging directives.
$ sudo sed -n '1,120p' /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf <VirtualHost *:80> ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost DocumentRoot /var/www/html ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined </VirtualHost> - Edit the default virtual host file to customize per-site directives.
$ sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
Incorrect syntax in /etc/apache2 can prevent apache2 from reloading and cause downtime.
- Modify the global Apache configuration when server-wide settings are needed.
$ sudo vi /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
- Test the configuration for errors before applying changes.
$ sudo apache2ctl configtest Syntax OK
Syntax OK indicates a valid configuration even when AH00558 is shown.
- Restart the Apache2 service to apply the changes.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Use sudo systemctl reload apache2 for a graceful reload when a full restart is unnecessary.
- Allow incoming HTTP traffic through UFW when a firewall is enabled.
$ sudo ufw allow http Rules updated Rules updated (v6)
Debian commonly uses nftables/iptables instead of UFW.
- Allow incoming HTTPS traffic through UFW when a firewall is enabled.
$ sudo ufw allow https Rules updated Rules updated (v6)
- Verify the default site responds locally over HTTP.
$ curl -sI http://127.0.0.1/ HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Mon, 29 Dec 2025 03:06:01 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.58 (Ubuntu) Last-Modified: Sun, 28 Dec 2025 06:15:52 GMT ETag: "29af-646fd0ef6f600" Accept-Ranges: bytes Content-Length: 10671 Vary: Accept-Encoding Content-Type: text/html

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
