Installing the Apache HTTP Server (httpd) provides a standard, well-supported way to serve websites and internal applications on CentOS, Red Hat, and Fedora. A correct base setup avoids common first-run problems like a service that starts but is unreachable due to firewall policy.
On these distributions, Apache is delivered as the httpd package and managed as the systemd unit httpd.service. Most server-wide settings live in /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf, while additional configuration and module snippets are commonly loaded from /etc/httpd/conf.d.
A working setup depends on three moving parts lining up: a valid configuration (checked with apachectl configtest), a running service (managed with systemctl), and network policy that permits inbound HTTP and HTTPS (typically firewalld). When serving content outside the default document root or listening on non-standard ports, SELinux contexts and port labeling may also need updates to prevent silent access denials.
Steps to install and configure Apache on CentOS, Red Hat or Fedora:
- Open a terminal with sudo privileges.
- Install the Apache package using the system package manager.
$ sudo dnf install --assumeyes httpd Last metadata expiration check: 0:02:40 ago on Sat 10 Jan 2026 12:54:52 PM +08. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Architecture Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: httpd aarch64 2.4.63-5.el10 appstream 49 k Installing dependencies: apr aarch64 1.7.5-3.el10 appstream 124 k apr-util aarch64 1.6.3-22.el10 appstream 97 k apr-util-lmdb aarch64 1.6.3-22.el10 appstream 13 k centos-logos-httpd noarch 100.2-3.el10 appstream 855 k httpd-core aarch64 2.4.63-5.el10 appstream 1.5 M httpd-filesystem noarch 2.4.63-5.el10 appstream 13 k httpd-tools aarch64 2.4.63-5.el10 appstream 82 k ##### snipped #####
On older CentOS releases that still use yum, replace dnf with yum.
- Configure Apache by editing its main configuration file.
$ sudo vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Setting a global ServerName (for example, ServerName example.com) suppresses the common fully-qualified domain name warning during config tests.
- Test the configuration for syntax errors.
$ sudo apachectl configtest AH00558: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using 127.0.1.1. Set the 'ServerName' directive globally to suppress this message Syntax OK
- Restart the httpd service to apply the configuration.
$ sudo systemctl restart httpd
- Verify the httpd service is running.
$ sudo systemctl is-active httpd active
- Enable the httpd service to start automatically on boot.
$ sudo systemctl enable httpd Created symlink '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service' → '/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service'.
Using systemctl enable --now httpd starts the service immediately while enabling it.
- Allow HTTP and HTTPS traffic through the firewall.
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http --add-service=https success
When firewalld is not installed or not used, apply equivalent rules in the active firewall stack.
- Reload the firewall to apply the new rules.
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload success
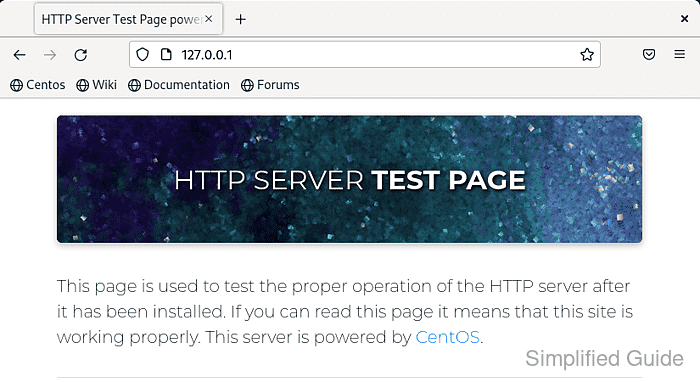
- Verify the Apache installation by requesting the default page locally.
$ curl -s 127.0.0.1 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en-US" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en-US"> <head> <meta name="generator" content="HTML Tidy for HTML5 for Linux version 5.8.0" /> <title>HTTP Server Test Page</title> <meta charset="utf-8" /> ##### snipped #####

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
