Hotlinking happens when third-party sites embed files hosted on the same server (most often images), shifting bandwidth costs and cache pressure onto the origin without serving the site’s pages. Blocking hotlink requests reduces unwanted traffic spikes, keeps response times steadier for legitimate visitors, and limits content reuse that bypasses intended context.
The Apache web server can mitigate hotlinking by evaluating the HTTP Referer header and applying conditional rules before static files are served. With mod_rewrite enabled, requests for specific file extensions can be rejected unless the request’s referer matches an approved domain list, and the policy can be scoped to only the directories that contain hotlinked assets.
The Referer header is optional and can be stripped or spoofed, so hotlink protection is a bandwidth-control technique rather than a strict access-control boundary. Regex patterns must be written carefully to avoid allowing look-alike domains (for example, yourdomain.com.evil.tld), and rules should tolerate modern referrer policies that often send only an origin. Defining the rules in the virtual host configuration is the most predictable approach; using .htaccess requires AllowOverride permissions for rewrite directives.
Related: How to enable or disable Apache modules
Related: How to test your Apache configuration
Steps to prevent hotlinking in Apache:
- Enable the mod_rewrite module for Apache.
$ sudo a2enmod rewrite Enabling module rewrite. To activate the new configuration, you need to run: systemctl restart apache2
- The a2enmod workflow is common on Debian and Ubuntu installations of Apache.
- On RHEL-family systems, mod_rewrite is often already available; module loading typically uses a LoadModule rewrite_module line, and the service name is commonly httpd.
Option Debian / Ubuntu openSUSE / SLES Fedora / CentOS / RHEL macOS (built-in or Homebrew) XAMPP Enable mod_rewrite a2enmod rewrite Often a2enmod rewrite Verify LoadModule rewrite_module Verify LoadModule rewrite_module Usually enabled Service name (systemd) apache2 apache2 httpd N/A (apachectl) N/A - Locate the filesystem directory that contains the media files to protect.
- Open the Apache site configuration that serves that directory.
$ sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
- Add rewrite rules that deny common image extensions when the Referer domain is not approved.
<Directory "/var/www/html/images"> RewriteEngine On RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^$ RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^https?://(www\.)?host\.example\.net(/|$) [NC] RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^https?://(www\.)?files\.example\.net(/|$) [NC] RewriteRule \.(?:jpe?g|png|gif|webp)$ - [F,NC,L] </Directory>
If the rules must live in a .htaccess file, omit the <Directory> wrapper and ensure the parent Apache configuration allows overrides (for example, AllowOverride FileInfo or AllowOverride All) for that directory.
A missing domain boundary or unescaped dot can allow look-alike referers (for example, yourdomain.com.evil.tld) to pass as “approved”; keep \. escapes and a boundary like ( /|$ ) in the regex.
Directive/Rule Description RewriteEngine On Enables mod_rewrite processing for the directory scope. RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^$ Applies the block only when a Referer header exists, which keeps direct requests (no referer) working. RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^https?://(www\.)?host\.example\.net(/|$) [NC] Allows the primary domain (with optional www) over HTTP or HTTPS, while preventing host.example.net.evil.tld matches. RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^https?://(www\.)?files\.example\.net(/|$) [NC] Allows an additional partner domain. RewriteRule \.(?:jpe?g|png|gif|webp)$ - [F,NC,L] Forbids requests for matching extensions when none of the allowed referers match; F returns 403 Forbidden, NC is case-insensitive, L stops processing. - Save the configuration file.
- Validate the Apache configuration syntax.
$ sudo apache2ctl configtest Syntax OK
- Restart the Apache service to apply the changes.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
- Send a request with an allowed Referer header.
$ curl --head --silent --referer "https://host.example.net/" "http://host.example.net/images/example.jpg" HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Sat, 10 Jan 2026 05:43:56 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.58 (Ubuntu) Last-Modified: Sat, 10 Jan 2026 05:43:56 GMT ETag: W/"d-6480220bc1ef0" Accept-Ranges: bytes Content-Length: 13 Content-Type: image/jpeg
Replace /images/example.jpg with a real file path that exists on the server.
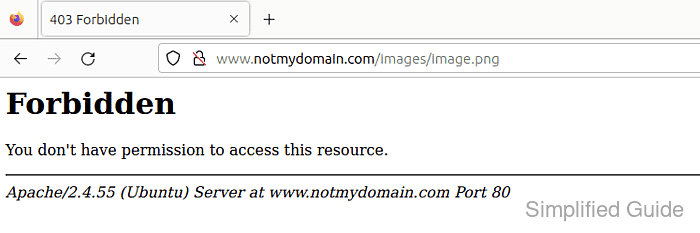
- Send a request with an unapproved Referer header.
$ curl --head --silent --referer "https://othersite.example/" "http://host.example.net/images/example.jpg" HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden Date: Sat, 10 Jan 2026 05:43:56 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.58 (Ubuntu) Content-Type: text/html; charset=iso-8859-1
Browser tests can be misleading due to cache and referrer policy; a curl request with --referer shows the server-side decision clearly.

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
