Configuring SSH to listen on multiple ports provides flexibility for environments that span different networks, firewalls, or access policies. Additional ports can separate administrative access, support alternative forwarding rules, or allow migration away from a heavily filtered default port without interrupting existing connections.
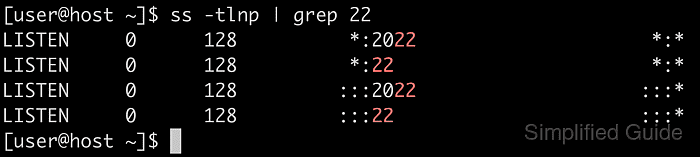
The sshd daemon reads listener definitions from the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file and creates a TCP listener for every Port directive it finds. When multiple Port lines are present, sshd binds to each of them on IPv4 and IPv6, subject to any restrictions imposed by the local firewall or access control lists.
Each additional port must be opened in the host firewall and permitted by any SELinux policy applied to sshd. Failing to update these layers can cause connections on the new port to hang or be rejected even though the daemon is running, and incorrect changes to listener settings can make remote logins impossible if no alternative access path is available.
Steps to run SSH server on multiple ports:
- Open a terminal session on the server with access to an account that can use sudo.
$ whoami user
Any account able to edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config and restart sshd is suitable.
- Inspect existing SSH listening ports to confirm that the additional port is free.
$ ss -tlnp | grep -E "22|2222" LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* users:(("sshd",pid=10704,fd=3),("systemd",pid=1,fd=297)) LISTEN 0 4096 [::]:22 [::]:* users:(("sshd",pid=10704,fd=4),("systemd",pid=1,fd=298))Output showing only port 22 indicates that port 2222 is not yet in use.
- Open the sshd configuration file in a text editor with elevated privileges.
$ sudo vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
vi is used here, but any preferred editor such as nano or vim works.
- Locate the existing Port directive near the top of the file or add one if it is missing.
Many distributions ship a commented example such as #Port 22; remove the leading # to activate it.
- Add a separate Port line for each TCP port that sshd should listen on.
Port 22 Port 2222
Each listener requires its own Port directive, and all active directives must remain uncommented.
A line beginning with # is treated as a comment and ignored, which can unintentionally disable a listener or leave only a nonstandard port active.
- Save the file and exit the editor after confirming that only the intended Port lines are present.
Retain at least one known-good port until connectivity on any new ports is verified.
- Validate the updated configuration before restarting the daemon.
$ sudo sshd -t
No output from sshd -t indicates that the configuration syntax is valid.
If an error message appears, revert or correct the changes before restarting sshd to avoid losing remote access.
- Permit the new port through the host firewall if filtering is enabled.
$ sudo ufw allow 2222/tcp Rules updated Rules updated (v6) $ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=2222/tcp --permanent success $ sudo firewall-cmd --reload success
Use the ufw command on systems that rely on UFW (commonly Ubuntu or Debian) and the firewalld commands on systems such as CentOS or Red Hat.
Exposing additional ports increases the attack surface, so combine these rules with network-level filtering and strong authentication.
- Register the new port with SELinux so that sshd is allowed to bind to it when enforcement is enabled.
$ sudo semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 2222
The ssh_port_t type labels the port for SSH traffic, aligning the listener with the existing security policy.
If semanage is not available, it can be installed on CentOS or Red Hat using a package such as policycoreutils-python or policycoreutils-python-utils, for example:
$ sudo yum install --assumeyes policycoreutils-python
- Restart the sshd service to apply the new listener configuration.
$ sudo systemctl restart ssh
Some distributions name the unit sshd instead of ssh; adjust the command accordingly if the restart fails with a unit-not-found error.
Restarting sshd replaces the running daemon, so invalid settings can prevent new logins even if current sessions remain open only temporarily.
- Confirm that the sshd service is running cleanly after the restart.
$ sudo systemctl status ssh ● ssh.service - OpenBSD Secure Shell server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/ssh.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Sun 2026-01-11 05:33:23 +08; 157ms ago Docs: man:sshd(8) man:sshd_config(5) Process: 15010 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/sshd -t (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 15013 (sshd) Tasks: 1 (limit: 4546) Memory: 2.7M (peak: 3.7M) CPU: 36ms CGroup: /system.slice/ssh.service └─15013 "sshd: /usr/sbin/sshd -D [listener] 0 of 10-100 startups" ##### snipped #####The Active: active (running) line confirms that the daemon started successfully with the new configuration.
- Verify that sshd is listening on all configured ports.
$ ss -tlnp | grep -E "22|2222" LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:2222 0.0.0.0:* users:(("sshd",pid=15013,fd=3)) LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* users:(("sshd",pid=15013,fd=5)) LISTEN 0 128 [::]:2222 [::]:* users:(("sshd",pid=15013,fd=4)) LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:* users:(("sshd",pid=15013,fd=6))Entries for both 22 and 2222 on IPv4 and IPv6 confirm that the SSH server is listening on multiple ports.
If the new port does not appear, review firewall and SELinux settings and inspect logs using journalctl for startup or binding errors.

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
