When working with Python, extracting specific components from a URL is a common task, especially in web scraping and similar applications. You'll often need to isolate elements like the hostname, domain name, or protocol to process the URL effectively. Understanding how to do this efficiently is crucial for handling web data.
The urllib module in Python provides the tools needed for this task. Using the urlparse function within this module, you can break down a URL into its parts, such as the scheme, network location, and path. This allows for easy extraction of the hostname or domain name from a given URL.
By using urlparse, you can focus on the relevant parts of the URL while discarding unnecessary information. This method is straightforward and effective for anyone working with web data in Python.
Steps to get a hostname from a URL using Python:
- Launch your preferred Python shell.
$ ipython3 Python 3.8.2 (default, Apr 27 2020, 15:53:34) Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information IPython 7.13.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.
- Import urllib.parse module.
In [1]: import urllib.parse
- Parse URL using urlparse function from urllib.parse module.
In [2]: parsed_url = urllib.parse.urlparse('https://www.example.com/page.html') - Print out parsed URL output.
In [3]: print(parsed_url) ParseResult(scheme='https', netloc='www.example.com', path='/page.html', params=//, query=//, fragment=//)
- Select required output and process accordingly.
In [4]: print(parsed_url.netloc) www.example.com
- Create a Python script that accepts a URL as parameter and outputs corresponding parsed URL.
- get-host-name-from-url.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3 import urllib.parse import sys url = sys.argv[1] parsed_url = urllib.parse.urlparse(url) print(parsed_url) print("Host name: ", parsed_url.netloc)
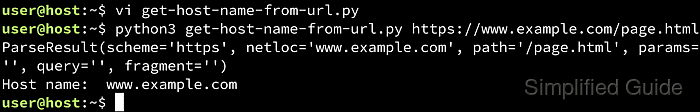
- Run the script from the command with URL as parameter.
$ python3 get-host-name-from-url.py https://www.example.com/page.html ParseResult(scheme='https', netloc='www.example.com', path='/page.html', params=//, query=//, fragment=//) Host name: www.example.com

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
