A proxy server makes it possible to reach a SSH server that cannot be contacted directly, such as a host inside a private network or behind restrictive firewall rules. The proxy acts as a relay for the initial TCP connection, while the SSH session stays end-to-end encrypted once the tunnel is established.

In PuTTY, proxy settings live under Connection → Proxy and apply to the current session profile. PuTTY can negotiate through common proxy protocols such as HTTP (CONNECT tunneling) and SOCKS (v4/v5), allowing the SSH transport to be carried through the proxy to the target server and port.
Proxy connectivity depends on policy as much as configuration; the proxy must be permitted to reach the destination port (commonly 22) and may require authentication. DNS resolution also matters: internal hostnames might only resolve from the proxy side, and the proxy handshake may fail before any SSH banner appears if the proxy blocks the request.
Steps to connect via proxy server in PuTTY:
- Launch PuTTY.
- Open the Proxy settings from the left sidebar under Connection.
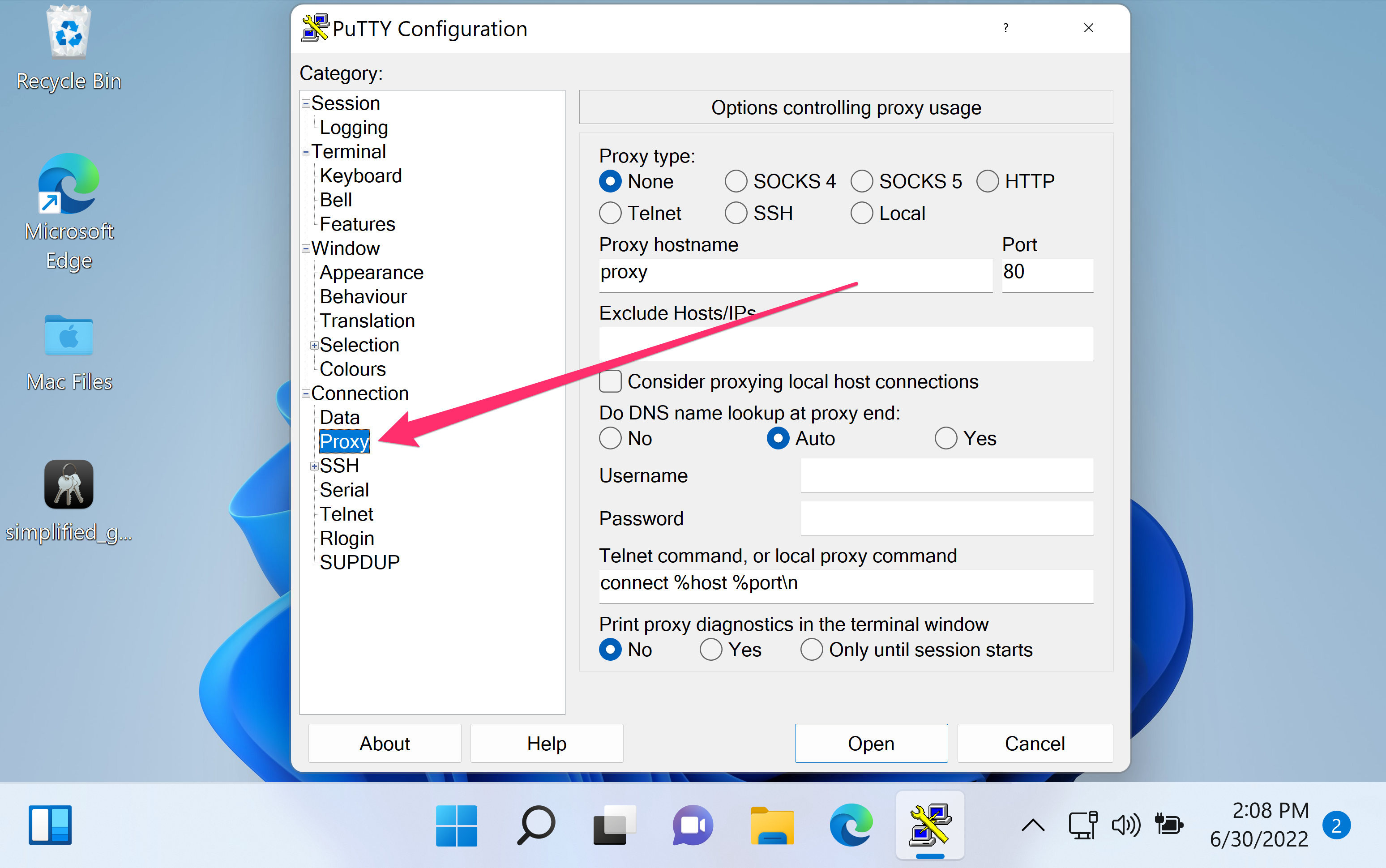
- Select the proxy type to match the proxy service.
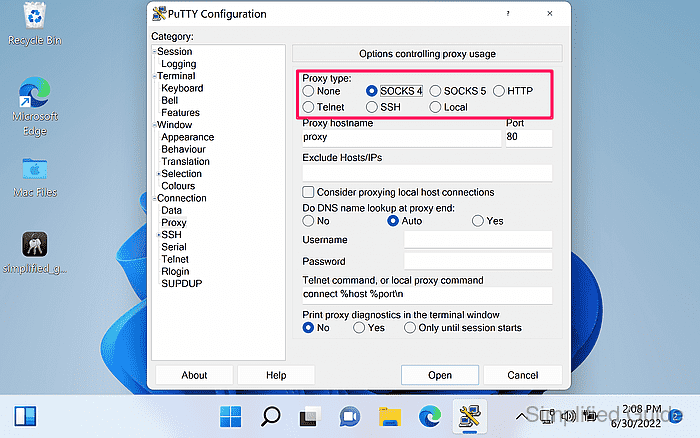
HTTP proxies typically require tunneling support (CONNECT), while SOCKS5 is commonly used for generic TCP forwarding.
- Enter the proxy hostname or IP address and the proxy port.
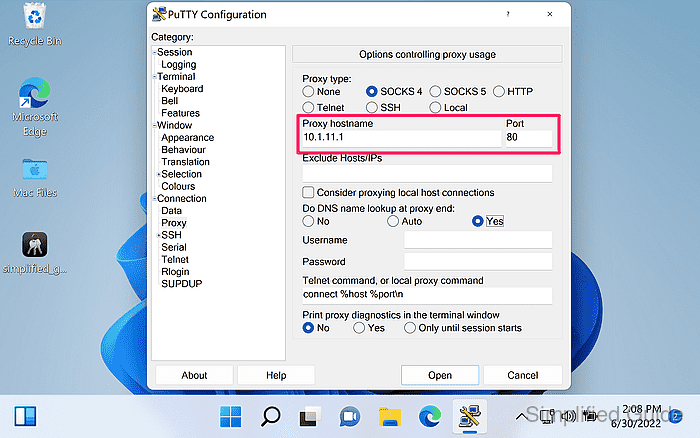
- Choose whether to resolve DNS locally or at the proxy end.
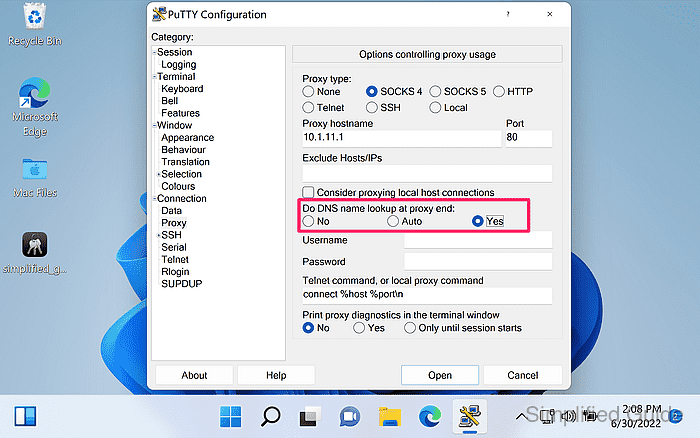
Enabling Do DNS name lookup at proxy end can be required when the target hostname only exists in the proxy-side network.
- Enter proxy credentials if the proxy requires authentication.
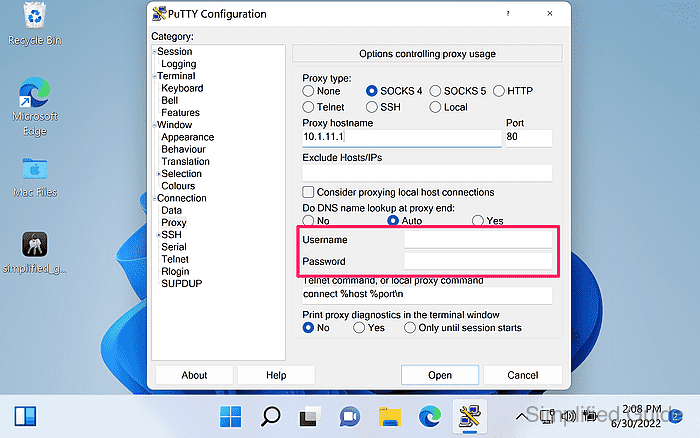
Proxy Username and Proxy Password are provided to the proxy during negotiation; avoid reusing privileged credentials on untrusted proxies.
- Return to the Session category in the left sidebar.
- Enter the target SSH server hostname or IP address in Host Name (or IP address).
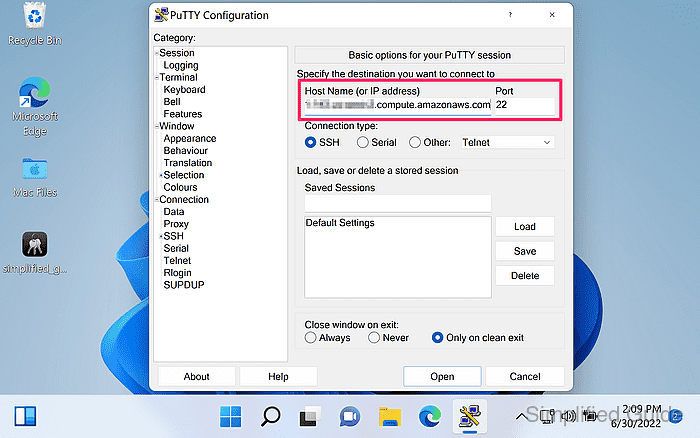
- Enter the target SSH port in Port if it is not the default 22.

- Click Open to start the proxied connection.
- Verify the server fingerprint at the host key security alert prompt and click Accept.

Accepting an unexpected host key can indicate a man-in-the-middle attack or a connection to the wrong server.
- Confirm the SSH login prompt appears in the PuTTY terminal window.

Proxy errors typically appear before any SSH banner, while SSH authentication prompts indicate the tunnel is working.

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
