In Linux environments, recursively listing files reveals the full structure of a directory tree, including nested subdirectories and hidden files. This kind of overview is useful when cleaning up old data, auditing deployments, or tracking down configuration files scattered across multiple levels.
Common tools such as ls, find, du, and tree implement recursion in slightly different ways. Some focus on displaying directory contents, others specialize in searching by name or attributes, and some summarize disk usage. Combining these tools makes it possible to both see the hierarchy and act on specific subsets of files.
Recursive operations can touch a large number of paths, which may produce very long outputs and increase disk I/O on busy systems. Access permissions, filesystem mounts, and symbolic links can also affect results, so commands often need to be run with sudo and, on very large trees, against carefully chosen subdirectories instead of the filesystem root.
Steps to recursively list files in Linux:
- Open a terminal in the target directory or specify the directory path when running commands.
$ pwd /root/sg-work
Commands in the following steps support any readable directory path, not just the current working directory.
- Use the ls command with the -R option to list files and subdirectories recursively.
$ ls -R recursive/ recursive/: subdirectory-01 subdirectory-02 recursive/subdirectory-01: file-01 file-02 file-03 recursive/subdirectory-02: file-01 file-02 file-03 $ ls -lR recursive/ recursive/: total 8 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 10 19:51 subdirectory-01 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 10 19:51 subdirectory-02 recursive/subdirectory-01: total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 10 19:51 file-01 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 10 19:51 file-02 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 10 19:51 file-03 recursive/subdirectory-02: total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 10 19:51 file-01 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 10 19:51 file-02 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 10 19:51 file-03
The -R flag recurses into each child directory; adding -l shows ownership, permissions, and timestamps.
- Display command usage for ls to review additional recursive and formatting options when needed.
$ ls --help Usage: ls [OPTION]... [FILE]... List information about the FILEs (the current directory by default). Sort entries alphabetically if none of -cftuvSUX nor --sort is specified. Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too. -a, --all do not ignore entries starting with . -A, --almost-all do not list implied . and .. --author with -l, print the author of each file -b, --escape print C-style escapes for nongraphic characters --block-size=SIZE with -l, scale sizes by SIZE when printing them; e.g., '--block-size=M'; see SIZE format below -B, --ignore-backups do not list implied entries ending with ~ ##### snipped #####Help output documents useful combinations such as -R with –group-directories-first or -h for human-readable sizes.
- Use the find command without extra predicates to obtain a simple recursive list of all paths.
$ find recursive/ recursive/ recursive/subdirectory-01 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-03 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-02 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-01 recursive/subdirectory-02 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-03 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-02 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-01
find follows the directory tree starting from the given path and prints every directory and file encountered.
- Add filters to find to match only certain files, such as by name pattern or type.
$ find recursive/ -type f -name "file-0[12]" recursive/subdirectory-01/file-02 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-01 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-02 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-01
Combining -type f with -name avoids listing directories when only regular files are needed.
- Use the -ls or -print actions with find for detailed file information or stable machine-readable output.
$ find recursive/ -ls 1704000 4 drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Jan 10 19:51 recursive/ 1704052 4 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 10 19:51 recursive/subdirectory-01 1704153 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 10 19:51 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-03 ##### snipped ##### $ find recursive/ -print recursive/ recursive/subdirectory-01 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-03 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-02 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-01 recursive/subdirectory-02 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-03 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-02 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-01
The -ls action prints permission bits, owners, sizes, and timestamps; -print guarantees every path is printed exactly once.
- Review find help output to discover advanced predicates such as size, age, or permission filters.
$ find --help Usage: find [-H] [-L] [-P] [-Olevel] [-D debugopts] [path...] [expression] Default path is the current directory; default expression is -print. Expression may consist of: operators, options, tests, and actions. Operators (decreasing precedence; -and is implicit where no others are given): ( EXPR ) ! EXPR -not EXPR EXPR1 -a EXPR2 EXPR1 -and EXPR2 EXPR1 -o EXPR2 EXPR1 -or EXPR2 EXPR1 , EXPR2 Positional options (always true): -daystart -follow -nowarn -regextype -warnPredicates such as -mtime, -size, and -perm make recursive listings double as powerful searches.
- Use the du command with the -a switch to list each file and directory with its disk usage.
$ du -a recursive/ 0 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-03 0 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-02 0 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-01 4 recursive/subdirectory-01 0 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-03 0 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-02 0 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-01 4 recursive/subdirectory-02 12 recursive/
Recursive du output helps correlate files with their contribution to total space usage.
- Show du help to discover options for human-readable units, depth limits, or excluding paths.
$ du --help Usage: du [OPTION]... [FILE]... or: du [OPTION]... --files0-from=F Summarize device usage of the set of FILEs, recursively for directories. Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too. -0, --null end each output line with NUL, not newline -a, --all write counts for all files, not just directories --apparent-size print apparent sizes rather than device usage; although the apparent size is usually smaller, it may be larger due to holes in ('sparse') files, internal fragmentation, indirect blocks, and the like -B, --block-size=SIZE scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g., ##### snipped #####Options such as -h and –max-depth keep output readable on large directory trees.
- Install the tree utility from the distribution package manager when a graphical directory tree view is preferred.
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt install --assume-yes tree
tree is not part of a minimal base system on many Linux distributions and may need explicit installation.
- Generate a hierarchical view with tree to visualize the directory structure.
$ tree --charset=ascii recursive/ recursive/ |-- subdirectory-01 | |-- file-01 | |-- file-02 | `-- file-03 `-- subdirectory-02 |-- file-01 |-- file-02 `-- file-03 3 directories, 6 filesUse tree for human-friendly inspection and find or du when scripting or performing detailed searches.
- Switch to full-path and indentation-free output modes in tree when the listing must be parsed by other tools.
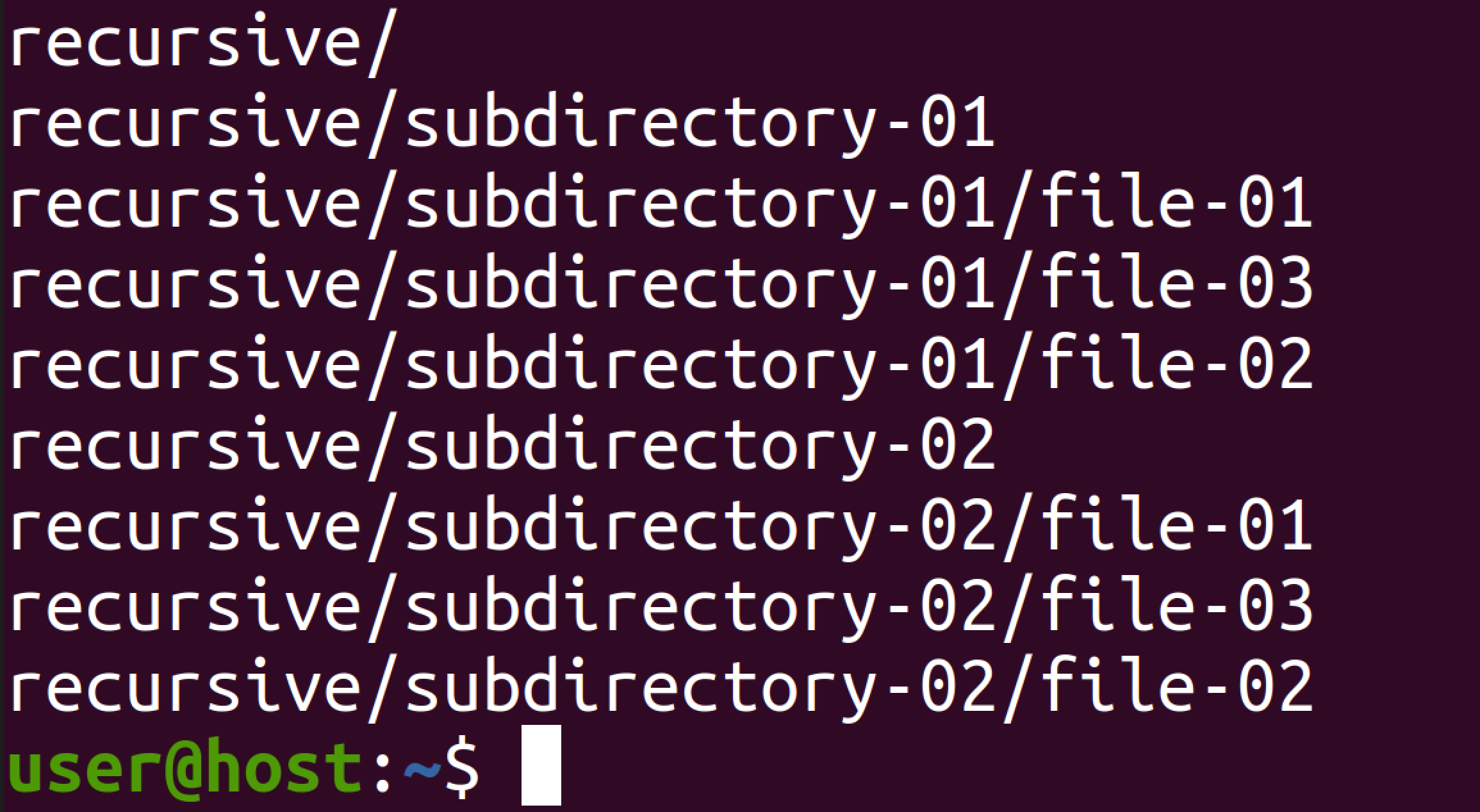
$ tree -i -f --charset=ascii recursive/ recursive recursive/subdirectory-01 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-01 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-02 recursive/subdirectory-01/file-03 recursive/subdirectory-02 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-01 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-02 recursive/subdirectory-02/file-03 3 directories, 6 files
The -f flag prints full paths and -i omits graphical indentation characters for easier post-processing.
- Display tree help for a summary of additional options such as pattern filters, depth limits, and HTML or JSON output.
$ tree --help usage: tree [-acdfghilnpqrstuvxACDFJQNSUX] [-L level [-R]] [-H baseHREF] [-T title] [-o filename] [-P pattern] [-I pattern] [--gitignore] [--gitfile[=]file] [--matchdirs] [--metafirst] [--ignore-case] ##### snipped #####
Advanced options enable export of recursive listings to XML, JSON, or HTML formats suitable for documentation or automation.
- Confirm recursion depth and performance on large directory trees by testing commands on a smaller subset before running them at the filesystem root.
$ find /var/log -maxdepth 3 -type f | wc -l 249
Running recursive commands such as find or tree on / or very large mount points can produce massive output and heavy disk I/O, which may impact system responsiveness.</WRAP>

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
