Reducing the information leaked by Apache makes automated fingerprinting harder and keeps version strings out of routine scans. Minimal banners do not fix vulnerabilities, but they do remove easy hints that help attackers match a target to known exploits. Many hardening baselines expect this basic reduction in exposed server details.
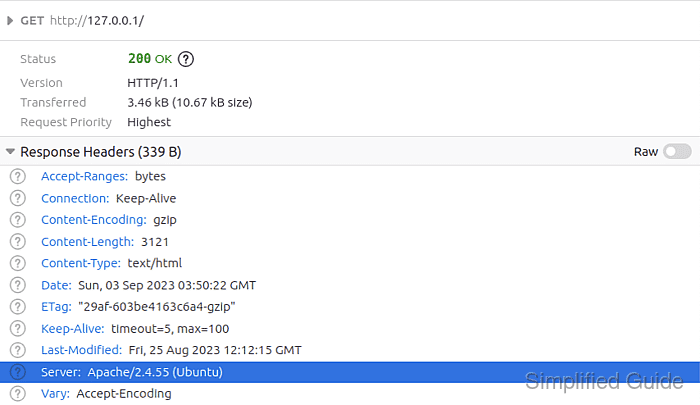
Two different mechanisms control what gets exposed. The Server HTTP response header is governed by ServerTokens, which determines whether the header includes only Apache or also includes version, OS, and module details. The HTML footer shown on server-generated pages (directory listings and default error documents) is governed by ServerSignature.
The steps below assume a Debian or Ubuntu layout with /etc/apache2 and the apache2 systemd unit name. Hidden banners still leave other identifying headers (application frameworks, reverse proxies, WAFs) untouched, so use this as a complement to patching, removing unused modules, and tightening configuration.
Related: How to test your Apache configuration
Related: How to enable or disable Apache modules
Steps to hide Apache server signatures:
- Open a terminal with sudo privileges.
- Find the current ServerTokens and ServerSignature settings in the Apache config tree.
$ sudo grep -RIn --include='*.conf' -E '^[[:space:]]*Server(Tokens|Signature)\b' /etc/apache2 /etc/apache2/conf-available/security.conf:12:ServerTokens OS /etc/apache2/conf-available/security.conf:23:ServerSignature On /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/security.conf:12:ServerTokens OS /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/security.conf:23:ServerSignature On ##### snipped #####
RHEL-style installs usually use /etc/httpd and the httpd unit name.
- Open /etc/apache2/conf-available/security.conf for editing.
$ sudoedit /etc/apache2/conf-available/security.conf
sudoedit uses $EDITOR and writes changes as the file is saved.
- Set ServerTokens to Prod in /etc/apache2/conf-available/security.conf.
ServerTokens Prod
Prod reduces the Server header to Apache rather than a detailed banner.
- Set ServerSignature to Off in /etc/apache2/conf-available/security.conf.
ServerSignature Off
ServerSignature controls the footer on server-generated error pages and directory listings.
Avoid multiple active ServerTokens or ServerSignature lines across included files, since the last one read takes effect.
- Save the file.
- Close the editor.
- Enable the security configuration snippet.
$ sudo a2enconf security Conf security already enabled
- Test the Apache configuration syntax.
$ sudo apache2ctl configtest AH00558: apache2: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using 127.0.1.1. Set the 'ServerName' directive globally to suppress this message Syntax OK
- Restart the Apache service to apply the changes.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Restarting apache2 briefly interrupts active connections.
- Verify the Server header no longer includes a version string.
$ curl -sI http://127.0.0.1/ HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Sat, 10 Jan 2026 05:42:13 GMT Server: Apache Last-Modified: Sat, 10 Jan 2026 05:32:07 GMT ETag: "29af-64801f6762249" Accept-Ranges: bytes Content-Length: 10671 Vary: Accept-Encoding Content-Type: text/html ##### snipped #####
Use the public hostname or the relevant VirtualHost address to validate what external clients actually see.
- Verify the default error page has no server signature footer.
$ curl -s http://127.0.0.1/does-not-exist <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN"> <html><head> <title>404 Not Found</title> </head><body> <h1>Not Found</h1> <p>The requested URL was not found on this server.</p> </body></html>
A custom ErrorDocument may return different HTML, but the Apache signature footer should remain absent.

Mohd Shakir Zakaria is a cloud architect with deep roots in software development and open-source advocacy. Certified in AWS, Red Hat, VMware, ITIL, and Linux, he specializes in designing and managing robust cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
